Predict log EC50s of Dual-Agonist Peptides using Convolutional Neural Network¶
The example in this paper is adapted from the following paper:
Puszkarska, A.M., Taddese, B., Revell, J. et al. Machine learning designs new GCGR/GLP-1R dual agonists with enhanced biological potency. Nat. Chem. (2024)
Here is the link to its original github repository PeptideModels
This paper aims to design dual-agonists peptides targeting human GCG and GLP-1 receptors. The loss function of the original model contains the MSE loss of peptide-GCGR log EC50 and the MSE loss of peptide-GLP-1R log EC50, for the purpose of multi-task learning.
[ ]:
!pip install wget seaborn tqdm
Import Packages¶
[2]:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import tqdm
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
mpl.rcParams["font.size"] = 24
mpl.rcParams["lines.linewidth"] = 2
[3]:
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Device:", device)
Device: cpu
Download & Load Dataset¶
[ ]:
!python -m wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/xuhuihuang/uwmadisonchem361/refs/heads/main/CNN_training_data.csv \
--output CNN_training_data.csv
[ ]:
filename = "CNN_training_data.csv"
df = pd.read_csv(filename)
df
Saved under CNN_training_data (4).csv
| pep_ID | EC50_T1 | EC50_LOG_T1 | EC50_T2 | EC50_LOG_T2 | Aligned_Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | seq_pep1 | 3.75 | -11.43 | 563.00 | -9.25 | HSQGTFTSDYSKYLDSRRAQDFVQWLEEGE |
| 1 | seq_pep2 | 18.50 | -10.73 | 552.00 | -9.26 | HSQGTFTSDYSKYLDSRRAEDFVQWLENGE |
| 2 | seq_pep3 | 3.51 | -11.45 | 252.00 | -9.60 | HSQGTFTSDYSKYLDSRRAEDFVQWLENT- |
| 3 | seq_pep4 | 50.50 | -10.30 | 6.03 | -11.22 | HSQGTFTSDYSKYLDSRRAEDFVQWLVAGG |
| 4 | seq_pep5 | 2.87 | -11.54 | 238.00 | -9.62 | HSQGTFTSDYSKYLDSRRAQDFVQWLEAEG |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 120 | seq_pep121 | 29000.00 | -7.54 | 9.62 | -11.02 | HGEGTFTSDVSSYMERQSVDEFIAWLLKGR |
| 121 | seq_pep122 | 29400.00 | -7.53 | 7.94 | -11.10 | HGEGTFTSDVSSYMESQLVDEFIAWLLKGR |
| 122 | seq_pep123 | 29500.00 | -7.53 | 29500.00 | -7.53 | HGEGTFTSDVSSYMEPQSTDEFIAWLLKGR |
| 123 | seq_pep124 | 29200.00 | -7.53 | 598.00 | -9.22 | HGEGTFTSDVSSYMDFQSLVEFLAWLLKGR |
| 124 | seq_pep125 | 1110.00 | -8.95 | 30200.00 | -7.52 | HGEGTFTSDLSKQMDFESLVLFLEWLDNG- |
125 rows × 6 columns
Create PyTorch Dataset¶
Convert sequence to onehot embedding¶
[5]:
def seq2onehot(sequence):
AMINOACIDS = 'ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY'
onehot = np.zeros((len(sequence), len(AMINOACIDS)+1))
aa_to_idx = {aa: idx for idx, aa in enumerate(AMINOACIDS)}
for i, aa in enumerate(sequence):
if aa in aa_to_idx:
onehot[i, aa_to_idx[aa]] = 1
else:
onehot[i, -1] = 1
return onehot
[6]:
seq = df.iloc[0]["Aligned_Sequence"]
print("Peptide sequence:", seq)
onehot = seq2onehot(seq)
print("Onehot Embedding:")
print(onehot)
Peptide sequence: HSQGTFTSDYSKYLDSRRAQDFVQWLEEGE
Onehot Embedding:
[[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
[7]:
class PeptideDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, df, encoder,
seq_col="Aligned_Sequence", target_cols=("EC50_LOG_T1", "EC50_LOG_T2")):
self.df = df
self.encoder = encoder
self.seq_col = seq_col
self.target_cols = target_cols
def __len__(self):
return len(self.df)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
row = self.df.iloc[idx]
sequence = row[self.seq_col]
onehot_sequence = self.encoder(sequence)
onehot_sequence = np.transpose(onehot_sequence)
label = [row[col] for col in self.target_cols]
return torch.tensor(onehot_sequence, dtype=float), torch.tensor(label, dtype=float).reshape(1, -1)
Split Dataset¶
[8]:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# training/validation dataset
data_size = df.shape[0]
test_ratio = 0.10
test_size = int(data_size*test_ratio)
train_indices, test_indices = train_test_split(range(data_size), test_size=test_size, shuffle=True)
print(f"Training size: {len(train_indices)}, test size: {len(test_indices)}")
train_df, test_df = df.iloc[train_indices], df.iloc[test_indices]
Training size: 113, test size: 12
[9]:
# create dataloaders
batch_size = 10
encoder = seq2onehot
train_data = PeptideDataset(train_df, encoder=encoder)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, drop_last=False)
test_data = PeptideDataset(test_df, encoder=encoder)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False, drop_last=False)
[10]:
## uncomment the block to see one datapoint
# train_data[0]
x, y = train_data[0]
print("Shape of one datapoint:", x.shape)
print("Shape of one label:", y.shape)
Shape of one datapoint: torch.Size([21, 30])
Shape of one label: torch.Size([1, 2])
CNN Model¶
[11]:
class BaseModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_shape, dropout=0.3):
super().__init__()
# Defining NN layers in Conv Block #1
in_channels = in_shape[0]
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=256)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout1d(p=dropout)
# Defining NN layers in Conv Block #2
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=512)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout1d(p=dropout)
# Defining NN layers in Conv Block #3
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=512, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=128)
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2)
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout1d(p=dropout)
#Explore the diemnsion in order to concatenate the data later
self._dummy_input_shape = (1, in_channels, in_shape[1])
self.dummy_input = torch.randn(self._dummy_input_shape)
self.flattened_size = self._calculate_flattened_size()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout1d(p=dropout)
# Defining fully connected layer (128 hidden neurons)
self.dense1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=self.flattened_size, out_features=128, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(),
)
# Defining fully connected layer (64 hidden neurons)
self.dense2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=128, out_features=64, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(),
)
def forward(self, input_seqs):
# Calling NN layers in Cov Block #1
x = self.dropout1(self.pool1(self.bn1(self.conv1(input_seqs))))
# Calling NN layers in Cov Block #2
x = self.dropout2(self.pool2(self.bn2(self.conv2(x))))
# Calling NN layers in Cov Block #3
x = self.dropout3(self.pool3(self.bn3(self.conv3(x))))
# Pooling and concatenate the data
length = x.shape[-1]
max_pool = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=length)(x).squeeze(-1)
avg_pool = nn.AvgPool1d(kernel_size=length)(x).squeeze(-1)
x = torch.cat([max_pool, avg_pool], dim=-1)
# Calling the dense NN layer #1
x = self.dropout(self.dense1(x))
# Calling the dense NN layer #2
x = self.dropout(self.dense2(x))
return x
def _calculate_flattened_size(self):
"""Pass dummy data through the network to get the flattened size."""
with torch.no_grad():
x = self.dummy_input
x = self.dropout1(self.pool1(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))))
x = self.dropout2(self.pool2(self.bn2(self.conv2(x))))
x = self.dropout3(self.pool3(self.bn3(self.conv3(x))))
# max pooling and average pooling layer here turn each 30-residude peptide into a single dimension.
# 128*1: "128" can be traced back to the original 20+1 type of amino acides
# while "1" refers to a whole peptide in order to predict properties of whole peptides
length = x.shape[-1]
max_pool = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=length)(x).squeeze(-1)
avg_pool = nn.AvgPool1d(kernel_size=length)(x).squeeze(-1)
x = torch.cat([max_pool, avg_pool], dim=-1)
return x.shape[1]
class MultiHeadModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_shape, dropout=0.3):
super().__init__()
self.base_model = BaseModel(in_shape=in_shape, dropout=dropout)
self.head_1 = nn.Linear(in_features=64, out_features=1, bias=True)
self.head_2 = nn.Linear(in_features=64, out_features=1, bias=True)
def forward(self, input_seqs):
base_out = self.base_model(input_seqs)
out_1 = self.head_1(base_out)
out_2 = self.head_2(base_out)
return torch.cat([out_1, out_2], dim=1)
[12]:
def train_one_epoch(model, criterion, optimizer, dataloader):
losses = []
model.train()
for x, y_true in dataloader:
if device == "cuda":
x, y_true = x.to(device), y_true.to(device)
x, y_true = x.float(), y_true.float()
optimizer.zero_grad()
y_pred = model(x) # Forward propagation is called here.
# MSE loss for linear regression
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_true.squeeze(1))
loss.backward() # Backprogation
optimizer.step()
losses.append(loss.cpu().detach().item())
return losses
def val_one_epoch(model, criterion, dataloader):
losses = []
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y_true in dataloader:
if device == "cuda":
x, y_true = x.to(device), y_true.to(device)
x, y_true = x.float(), y_true.float()
y_pred = model(x)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_true.squeeze(1))
losses.append(loss.cpu().detach().item())
return losses
loss function¶
[13]:
def multi_task_loss(y_pred, y_true):
y1_pred, y1_true = y_pred[:, 0], y_true[:, 0]
y2_pred, y2_true = y_pred[:, -1], y_true[:, -1]
mse1 = nn.MSELoss()(y1_pred, y1_true)
mse2 = nn.MSELoss()(y2_pred, y2_true)
return 0.5 * mse1 + 0.5 * mse2
Training¶
[14]:
model = MultiHeadModel(in_shape=(21, 30))
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
print(f"Total number of parameters: {total_params}")
model = model.to(device)
model = model.float()
criterion = multi_task_loss
# using a gradient descsent based method for optimiztion
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
n_epochs = 1500
Total number of parameters: 649026
[15]:
train_loss = []
val_loss = []
for epoch in tqdm.tqdm(range(n_epochs)):
losses = train_one_epoch(model, criterion, optimizer, train_loader)
train_loss.append(np.mean(losses))
losses = val_one_epoch(model, criterion, test_loader)
val_loss.append(np.mean(losses))
100%|██████████| 1500/1500 [09:23<00:00, 2.66it/s]
[16]:
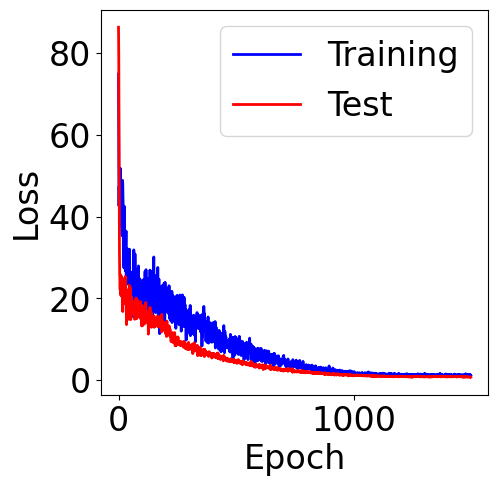
f, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5,5))
ax.plot(train_loss, c="blue", label="Training")
ax.plot(val_loss, c="red", label="Test")
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend()
[16]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7c9f3213df10>
Evaluation metrics¶
[17]:
y1_true = []
y1_pred = []
y2_true = []
y2_pred = []
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for x,y in test_loader:
if device == "cuda":
x = x.to(device)
x = x.float()
y_pred = model(x)
y1_pred.extend([y_pred[i, 0].item() for i in range(len(y_pred))])
y2_pred.extend([y_pred[i, 1].item() for i in range(len(y_pred))])
y = y.reshape(y_pred.shape)
y1_true.extend([y[i, 0].item() for i in range(len(y))])
y2_true.extend([y[i, 1].item() for i in range(len(y))])
[18]:
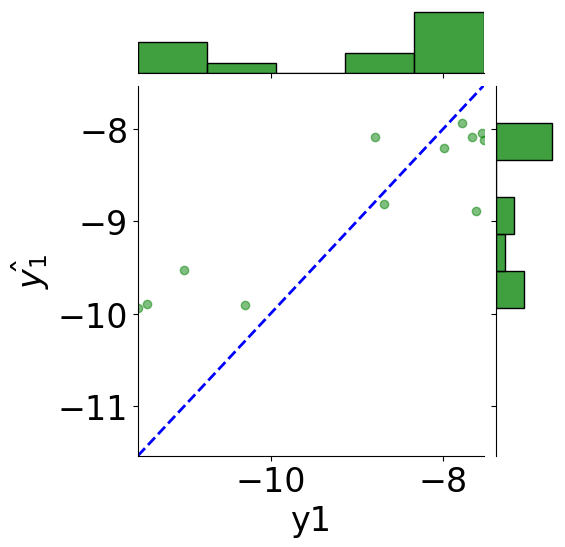
tmp_df = pd.DataFrame({"y1": y1_true, r"$\hat{y_1}$": y1_pred,
"y2": y2_true, r"$\hat{y_2}$": y2_pred})
# scatter plot
g = sns.JointGrid(x="y1", y=r"$\hat{y_1}$", data=tmp_df)
g = g.plot_joint(plt.scatter, c="green", alpha=0.5)
# line: y_pred = y
y_line = np.linspace(np.min(y1_true), np.max(y1_true), 200)
g.ax_joint.plot(y_line, y_line, color="blue", linestyle="--");
# histograms
g = g.plot_marginals(sns.histplot, data=df, color="green", kde=False)
g.ax_joint.set_xlim(np.min(y_line), np.max(y_line))
g.ax_joint.set_ylim(np.min(y_line), np.max(y_line))
plt.show()
[19]:
print(f"MSE: {mean_squared_error(y1_true, y1_pred):.2f}")
print(f"Coefficient of determination: {r2_score(y1_true, y1_pred):.2f}")
MSE: 0.85
Coefficient of determination: 0.64
[20]:
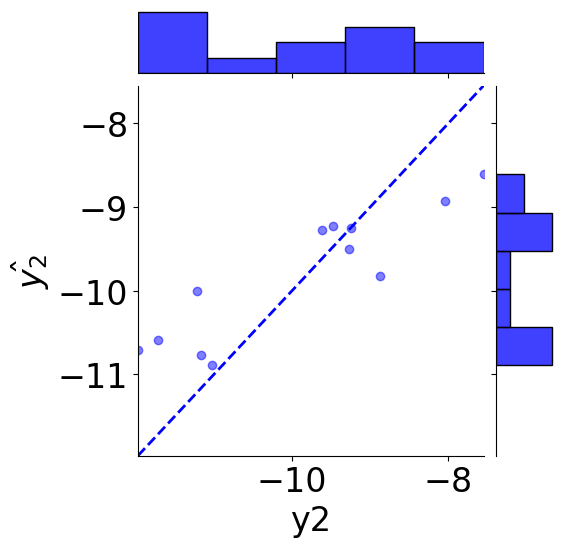
# scatter plot
g = sns.JointGrid(x="y2", y=r"$\hat{y_2}$", data=tmp_df)
g = g.plot_joint(plt.scatter, c="blue", alpha=0.5, label="GLP-1R")
# line: y_pred = y
y_line = np.linspace(np.min(y2_true), np.max(y2_true), 200)
g.ax_joint.plot(y_line, y_line, color="blue", linestyle="--");
# histograms
g = g.plot_marginals(sns.histplot, data=df, color="blue", kde=False)
g.ax_joint.set_xlim(np.min(y_line), np.max(y_line))
g.ax_joint.set_ylim(np.min(y_line), np.max(y_line))
plt.show()
[21]:
print(f"MSE: {mean_squared_error(y2_true, y2_pred):.2f}")
print(f"Coefficient of determination: {r2_score(y2_true, y2_pred):.2f}")
MSE: 0.63
Coefficient of determination: 0.67
[21]: