A simple nonlinear dataset: XOR¶
[1]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
cmap = plt.get_cmap('tab10')
colors = [cmap(i) for i in range(cmap.N)]
mpl.rcParams["font.size"] = 24
mpl.rcParams["lines.linewidth"] = 2
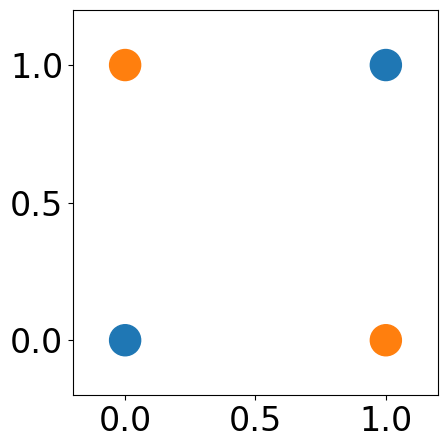
XOR Dataset¶
[2]:
X = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])
Y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0])
[3]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 5))
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=[colors[Y[i]] for i in range(len(Y))], s=500)
plt.xlim([-0.2, 1.2])
plt.ylim([-0.2, 1.2])
fig.tight_layout()
PyTorch implementation¶
[4]:
import torch
class LinearRegresion(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, indim):
super(LinearRegresion, self).__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(indim, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear(x)
return x
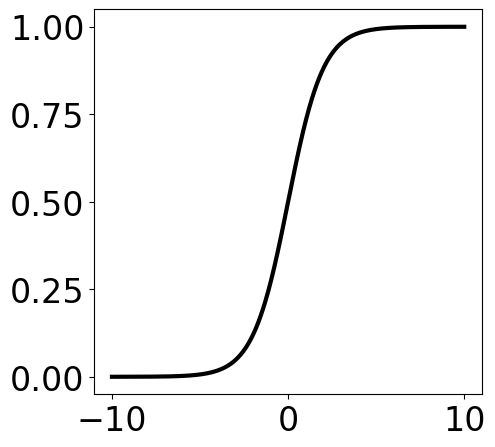
Logistic Regression¶
[5]:
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 1000)
y = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 5))
plt.plot(x, y, "k-", linewidth=3)
[5]:
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7dda427cf550>]
[6]:
model = LinearRegresion(2)
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
train_loss = []
data = torch.from_numpy(X).float()
y_true = torch.from_numpy(Y).float()
for epoch in range(500):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
y_pred = torch.sigmoid(output)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_true.reshape(y_pred.shape))
train_loss.append(loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
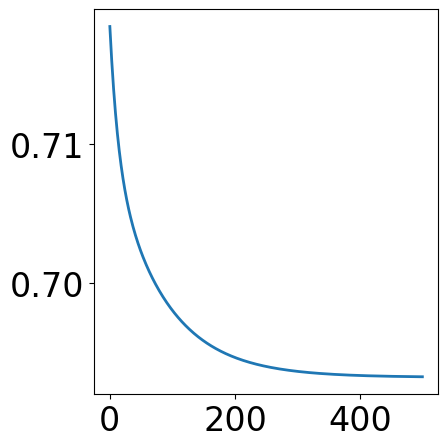
[7]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 5))
plt.plot(train_loss)
fig.tight_layout()
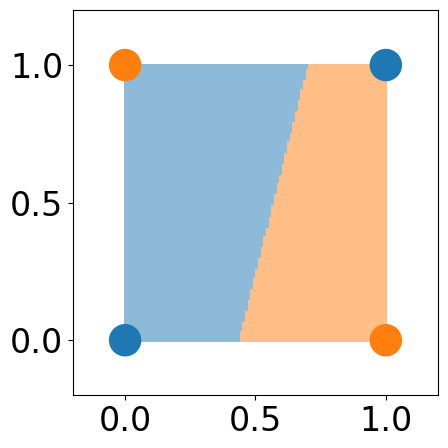
[8]:
x1 = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
x2 = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(x1, x2)
x_grid = np.hstack([xx1.ravel().reshape(-1, 1), xx2.ravel().reshape(-1, 1)])
x_grid = torch.from_numpy(x_grid).float()
output = model(x_grid)
y_grid_pred = torch.sigmoid(output)
y_grid_pred = y_grid_pred.reshape(xx1.shape)
# plot space separation
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 5))
custom_cmap = ListedColormap([cmap(0), cmap(1)])
plt.pcolormesh(xx1, xx2, y_grid_pred>=0.5, cmap=custom_cmap, alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=[colors[Y[i]] for i in range(len(Y))], s=500)
plt.xlim([-0.2, 1.2])
plt.ylim([-0.2, 1.2])
fig.tight_layout()
Multiple layer Perceptron¶
[9]:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class MLPRegresion(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, indim, hidden_dims):
assert isinstance(hidden_dims, list), f"Hidden dimensions {hidden_dims} should be a list"
super(MLPRegresion, self).__init__()
hidden_dims = [indim] + hidden_dims
layers = []
for i in range(len(hidden_dims)-1):
layers.append(torch.nn.Linear(hidden_dims[i], hidden_dims[i+1]))
layers.append(torch.nn.Linear(hidden_dims[-1], 1))
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(layers)
def forward( self, x):
for layer in self.layers[:-1]:
x = layer(x)
x = nn.ReLU()(x)
x = self.layers[-1](x)
return x
[10]:
model = MLPRegresion(2, [3, 2])
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
train_loss = []
data = torch.from_numpy(X).float()
y_true = torch.from_numpy(Y).float()
for epoch in range(5000):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
y_pred = torch.sigmoid(output)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_true.reshape(y_pred.shape))
train_loss.append(loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
[11]:
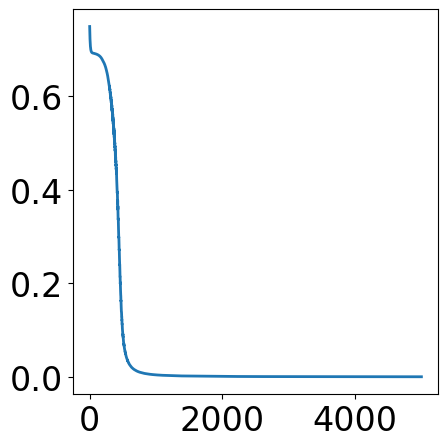
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 5))
plt.plot(train_loss)
fig.tight_layout()
[12]:
x1 = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
x2 = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(x1, x2)
x_grid = np.hstack([xx1.ravel().reshape(-1, 1), xx2.ravel().reshape(-1, 1)])
x_grid = torch.from_numpy(x_grid).float()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(x_grid)
y_grid_pred = torch.sigmoid(output)
y_grid_pred = y_grid_pred.reshape(xx1.shape)
# plot space separation
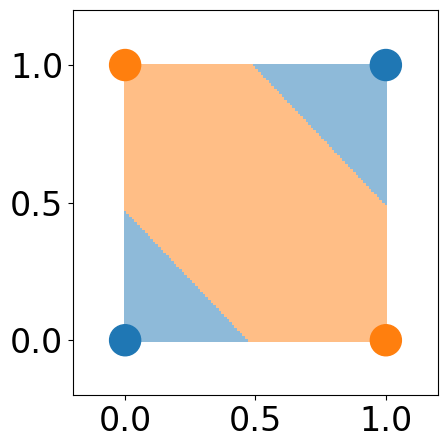
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 5))
custom_cmap = ListedColormap([cmap(0), cmap(1)])
plt.pcolormesh(xx1, xx2, y_grid_pred>=0.5, cmap=custom_cmap, alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=[colors[Y[i]] for i in range(len(Y))], s=500)
plt.xlim([-0.2, 1.2])
plt.ylim([-0.2, 1.2])
fig.tight_layout()
[12]: